DCF (Distributed Coordination Function)
This is the main medium access method used by 802.11 stations using CSMA-CA technique as mention in my earlier post regarding CSMA-CA. When AP functions in DCF mode, it is called CP (Contention Period).
PCF (Point Coordination Function)
This is an optional access method that is used along with DCF by the AP called CFP (Contention Free Period). Here the AP polls the clients in PCF mode to send data in the medium during CFP.
BSS (Basic Service Set)
A BSS of an AP comprises of a single AP with one or more 802.11 clients. Each BSS has a unique identifier called BSSID that is the radio mac address of the AP with 48 bits. For example.
An AP with one radio has one BSSID and AP with two radio has two BSSIDs
BSA (Basic Service Area) is the physical coverage provided by the AP’s BSS for associated clients to remain connected even if they move within the BSS.
ESS (Extended Service Set)
An ESS is a combination of multiple APs with their BSSs where the APs have to have a partial overlap of 15-25 % (i.e. as per the recommendations for a good Wifi design) for seamless roaming of clients between the APs.
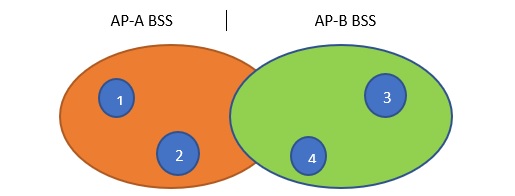
The above demonstrates two APs: A, B BSS. They form an ESS due to the overlap of their BSS. Due to this overlap of BSS, the client devices: 1,2,3,4 can roam between APs: A and B without disconnection.
SSID (Service Set Identifier)
This refers to the logical name used to identify a wireless network.
RSSI (Received Signal Indicator)
According to CWNP books, this is an indicator that is used by the 802.11 devices as a relative measurement of the received signal strength. This varies between various vendor devices. For example.
One vendor dot11 device might use 0 – 100 where 50 represents -25 dBm. Another vendor could use 0-60 where 30 could represent -25 dBm.
However, many vendors like Cisco use the term RSSI to mention about the received signal strength; instead of range of values. Received signal strength is represented as a negative value.
Noise Floor
Noise floor represents the unwanted signal that can corrupt or distort the actual signal being transmitted by the sender and hence deteriorating the signal quality. This is a negative value.
SNR (Signal to Noise Ratio)
This term refers to the actual signal quality after deducting the noise from the received signal strength. It is the difference between received signal strength and noise floor. This is a positive value.
SNR = Received Signal Strength – Noise floor
Antenna Gain
This is a passive gain that refers to the increase in power of the RF signal transmitted by changing the antenna direction to focus the RF energy.
EIRP (Equivalent Isotropic Radiated Power)
The highest RF signal strength that is transmitted from an AP antenna is the EIRP. This value depends on the regulatory domain of the country where the AP is deployed.
Radio Bands
In dot11 technology, there are two radio bands – 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz.
| 2.4 GHz (Unlicensed band) | 5 GHz (Unlicensed band) |
| Lot of legacy devices support this radio and not the 5 GHz | Most of the latest devices are dual band capable |
| It provides greater coverage and less speed compared to 5 GHz band | Provides less coverage and more speed compared to 2.4 GHz band |
| Modulation: DSSS in .11b HR/DSSS, ERP in .11g,n | OFDM in .11ac, OFDMA in .11ax |
| Only 3 non-overlapping channels: 1,6,11 that are available for dot11 devices to connect. | More number of available channels compared to 2.4 GHz – 36,40,44,48,52,56,60,64,68,96,100,104,108, 112,116,120,124,128,132, 136,140,144, 149,153,157,161,165.169 |
| Supported wireless technologies: 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, 802.11ax | Supported wireless technologies: 802.11a,802.11n, 802.11ac, 802.11 ax |
However, in reality, it is not possible to utilize all the 5 GHz channels since many channels are used for radar detection called DFS (Dynamic Frequency Selection). If a RADAR signal is detected, then the 802.11 station using DFS channel will be disconnected from that channel and forced to use another available channel. Hence, it is not preferred to use DFS channel for normal 802.11 operation.
DFS channels: 52,56,60,64,68,96,100,104,108, 112,116,120,124,128,132, 136,140,144
References:
CWNA Official Study Guide
CWAP Official Study Guide